Leukemia affects blood and bone marrow, disrupting the normal production of white blood cells. This condition can lead to severe complications if not managed with a well-structured nursing care plan. Nurses play a vital role in guiding patient care through clear assessments, accurate diagnoses, and targeted interventions. This article refreshes current insights on nursing care plans for leukemia and includes sample nursing care plans to serve as practical examples for clinical practice.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!
1. Introduction
Leukemia is a type of cancer that disrupts the normal function of blood cells. Nurses rely on a detailed care plan to standardize treatment, monitor patient progress, and adjust interventions as needed. Recent research and expert websites confirm that a structured nursing care plan improves patient safety and outcomes. This article explains the essential elements of a nursing care plan for leukemia, presents practical sample care plans, and offers tips on key nursing interventions. The content uses clear language and a straightforward subject-verb-object (SVO) sentence structure to ensure clarity and enhance search engine optimization.


2. Understanding Leukemia
Leukemia is a cancer that starts in the bone marrow and affects blood-forming tissues. The disease causes abnormal white blood cells to grow and multiply rapidly. These abnormal cells crowd out healthy blood cells and lead to symptoms such as fatigue, fever, weight loss, and bleeding. The condition can present in several forms, including acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Early diagnosis and ongoing management are critical. Nurses must understand the disease process to develop effective care plans that address the risks and challenges faced by patients.
3. Pathophysiology of Leukemia
The disease originates from genetic mutations in hematopoietic stem cells, leading to uncontrolled production of immature or abnormal white blood cells:
- Bone Marrow Crowding: Normal cells are displaced, reducing production of healthy red blood cells, platelets, and other white blood cells.
- Infiltrative Damage: Leukemic cells can infiltrate organs, causing diverse symptoms like lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, or neurological symptoms.
- Immune Suppression: The immune system becomes compromised, increasing infection risk.
4. Etiology of Leukemia
While the exact cause remains elusive, known risk factors include:
- Genetic Predispositions: Certain genetic syndromes like Down syndrome increase risk.
- Environmental Exposures: Radiation, chemotherapy, and exposure to certain chemicals like benzene.
- Viral Infections: Some evidence suggests links with viruses like HTLV-1 for certain types of leukemia.
5. Signs and Symptoms of Leukemia
Patients might experience:
- Fatigue and Weakness: Due to anemia from reduced red blood cell count.
- Increased Infection: From a lack of functional white blood cells.
- Bleeding or Bruising: Resulting from low platelet counts (thrombocytopenia).
- Bone Pain: Often from marrow expansion or infiltration.
- Lymph Node Enlargement: Palpable lymph nodes due to leukemic cell accumulation.
6. Nursing Diagnosis for Leukemia
Common diagnoses using NANDA guidelines include:
- Risk for Infection related to immunosuppression.
- Fatigue due to anemia.
- Risk for Bleeding associated with thrombocytopenia.
- Acute Pain from bone marrow infiltration or treatment side effects.
- Impaired Skin Integrity from frequent venipunctures or infections.
- Deficient Knowledge about the disease, treatment, and self-care.
7. Developing a Nursing Care Plan for Leukemia
A nursing care plan for leukemia provides a structured approach that covers assessment, diagnosis, planning, intervention, and evaluation. This plan guides nurses through several essential steps:
- Assessment: Nurses collect detailed patient histories, perform physical examinations, and review laboratory results such as complete blood count (CBC) and bone marrow biopsy reports. They note symptoms like fever, pallor, and bleeding tendencies.
- Nursing Diagnosis: Using NANDA guidelines, nurses identify common problems such as risk for infection, impaired tissue perfusion due to anemia, acute pain, and anxiety related to treatment. These diagnoses form the basis of the care plan.
- Planning: Nurses set clear, measurable goals. Goals include stabilizing vital signs, reducing infection risk, increasing hemoglobin levels, and alleviating pain. Each goal is designed to meet short-term and long-term patient needs.
- Intervention: Interventions include administering medications (such as chemotherapy, antibiotics, or blood transfusions), monitoring vital signs, providing nutritional support, and teaching self-care techniques. Nurses also follow strict infection control protocols.
- Evaluation: Nurses regularly review patient outcomes against the set goals. They use follow-up tests, patient feedback, and continuous assessments to adjust the care plan as needed.
This structured process helps standardize care and ensures that all aspects of patient needs are addressed effectively.
8. Key Nursing Interventions and Management
Research from authoritative sources highlights several key interventions that form the backbone of effective nursing management for leukemia patients:
- Vital Sign Monitoring: Nurses check temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure frequently. These measures help detect early signs of infection or bleeding. Early detection prevents complications.
- Medication Administration: Nurses deliver chemotherapy, antibiotics, and supportive medications following prescribed protocols. They monitor for side effects and adjust dosages based on patient response.
- Infection Control: Due to the risk of immunosuppression, nurses enforce rigorous hygiene practices. They educate patients about proper hand washing and isolation techniques.
- Blood Transfusions and Oxygen Support: For patients with anemia, nurses arrange for blood transfusions and provide supplemental oxygen. These measures improve oxygen delivery to tissues and reduce fatigue.
- Pain Management: Nurses assess pain levels and administer analgesics to alleviate discomfort. Effective pain management improves mobility and overall quality of life.
- Nutritional Support: Nurses encourage a balanced diet rich in iron and vitamins to support recovery. They collaborate with dietitians to develop individualized nutritional plans.
- Psychosocial Support: Nurses provide emotional support and counseling to help patients cope with anxiety and depression. They also connect patients with support groups and other resources.
These interventions address both the physical and emotional needs of patients, ensuring comprehensive care throughout the treatment process.
9. Sample Nursing Care Plans for leukemia
Below are two sample nursing care plans for leukemia patients. These examples use a clear 7‑column format that guides nursing actions from assessment through evaluation.
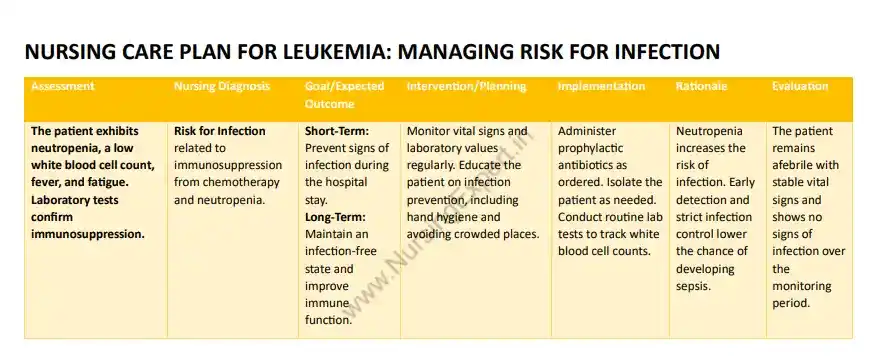
Sample Nursing Care Plan 1: Managing Risk for Infection
| Assessment | Nursing Diagnosis | Goal/Expected Outcome | Intervention/Planning | Implementation | Rationale | Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The patient exhibits neutropenia, a low white blood cell count, fever, and fatigue. Laboratory tests confirm immunosuppression. | Risk for Infection related to immunosuppression from chemotherapy and neutropenia. | Short-Term: Prevent signs of infection during the hospital stay. Long-Term: Maintain an infection-free state and improve immune function. | Monitor vital signs and laboratory values regularly. Educate the patient on infection prevention, including hand hygiene and avoiding crowded places. | Administer prophylactic antibiotics as ordered. Isolate the patient as needed. Conduct routine lab tests to track white blood cell counts. | Neutropenia increases the risk of infection. Early detection and strict infection control lower the chance of developing sepsis. | The patient remains afebrile with stable vital signs and shows no signs of infection over the monitoring period. |
Sample Nursing Care Plan 2: Improving Tissue Perfusion in Anemic Patients
| Assessment | Nursing Diagnosis | Goal/Expected Outcome | Intervention/Planning | Implementation | Rationale | Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The patient reports fatigue, pallor, and shortness of breath. Laboratory tests reveal a low hemoglobin level. | Impaired Tissue Perfusion related to anemia secondary to leukemia and its treatment. | Short-Term: Increase hemoglobin levels and improve oxygenation within 48 hours. Long-Term: Enhance tissue oxygen delivery and reduce symptoms of fatigue. | Plan for blood transfusions as ordered. Monitor oxygen saturation and vital signs frequently. Provide supplemental oxygen and educate on an iron-rich diet. | Administer the blood transfusion following established protocols. Check vital signs before, during, and after the procedure. Advise the patient on nutritional modifications. | Blood transfusions raise hemoglobin levels, which improves oxygen delivery. Supplemental oxygen meets immediate needs. | Post-transfusion, laboratory tests show an increased hemoglobin level, and the patient reports reduced fatigue and improved energy levels. |
These sample care plans illustrate how nurses can manage specific challenges in leukemia care. They guide interventions in a structured manner and help achieve targeted patient outcomes.
10. NURSING CARE PLAN FOR LEUKEMIA PDF DOWNLOAD
Access our comprehensive NURSING CARE PLAN FOR LEUKEMIA PDF DOWNLOAD to enhance your clinical practice and exam preparation. This detailed resource outlines every step of patient assessment, nursing diagnosis, planning, intervention, and evaluation tailored specifically for leukemia care. The PDF download provides clear guidelines and evidence-based strategies to manage leukemia effectively, ensuring that you deliver consistent, high-quality care.
Take advantage of this easy-to-use tool to streamline your workflow and improve patient outcomes. Click the link below to download your free copy now and transform your approach to leukemia management.
Download Your Nursing Care Plan for Leukemia PDF Now
11. Patient and Family Education
Patient education forms an essential part of the care plan. Nurses educate patients and their families on several key topics:
- Understanding Leukemia:
Nurses explain that leukemia is a cancer affecting the blood and bone marrow. They describe the impact of the disease on blood cell production and overall health. - Medication Management:
Nurses instruct patients on the correct administration of medications. They emphasize the importance of adhering to chemotherapy schedules and taking supportive drugs as prescribed. - Infection Control:
Education on infection prevention is critical. Nurses teach patients proper hand washing techniques, the use of personal protective equipment, and the importance of avoiding exposure to infections. - Nutritional Guidelines:
Nurses advise patients on maintaining a balanced diet rich in iron, vitamins, and proteins. They explain how proper nutrition can help support the immune system and promote recovery. - Symptom Monitoring:
Nurses teach patients how to monitor their symptoms. They advise on what signs to report immediately, such as high fever, severe pain, or sudden changes in condition. - Emotional Support:
Nurses provide counseling and support to help patients and families manage the emotional impact of the disease. They encourage participation in support groups and regular follow-up consultations.
Clear and consistent education empowers patients. It also helps families understand the disease and participate actively in the care process.
12. Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Effective management of leukemia requires a collaborative team effort. Nurses coordinate with various professionals to ensure comprehensive patient care. The following professionals play key roles:
- Oncologists:
Oncologists lead the treatment plan by prescribing chemotherapy, radiation, and other therapies. They review patient progress and adjust treatment as necessary. - Pharmacists:
Pharmacists review medication orders and ensure correct dosages. They also check for potential drug interactions and advise on medication administration. - Dietitians:
Dietitians develop individualized nutritional plans that support the patient’s immune system and overall health. They educate patients on healthy eating habits. - Social Workers:
Social workers assist patients with emotional and financial support. They help arrange resources, transportation, and counseling services. - Physical Therapists:
Physical therapists develop exercise programs that help maintain mobility and reduce fatigue. They work with patients to improve overall physical function.
Collaboration among these professionals improves communication, enhances treatment consistency, and leads to better patient outcomes.
13. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is leukemia?
Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. It leads to the abnormal production of white blood cells. - Why is a nursing care plan important for leukemia patients?
A nursing care plan standardizes patient care by outlining specific assessments, interventions, and evaluations. It helps reduce complications and improves patient outcomes. - What common nursing diagnoses are used in leukemia care?
Common diagnoses include risk for infection, impaired tissue perfusion due to anemia, acute pain, and anxiety related to treatment. - What key interventions do nurses perform for leukemia patients?
Nurses monitor vital signs, administer medications, enforce infection control, provide nutritional support, and offer psychosocial support. - How do nurses evaluate the success of a nursing care plan for leukemia?
Nurses assess patient progress through lab tests, vital signs, and feedback. They review if the set goals are met and adjust the plan accordingly.
14. Conclusion
A well-crafted nursing care plan for leukemia enhances patient safety and improves overall outcomes. Nurses use clear assessments, targeted interventions, and continuous education to manage symptoms and reduce complications. Through structured care plans and interdisciplinary collaboration, nurses ensure that leukemia patients receive comprehensive and timely care.
15. References and Sources
- American Cancer Society. Leukemia. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.org/cancer/leukemia.html
- Leukemia & Lymphoma Society. Understanding Leukemia. Retrieved from https://www.lls.org/leukemia
- MedlinePlus. Leukemia. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov/leukemia.html
- National Cancer Institute. Leukemia Overview. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.gov/types/leukemia
- Nursing Center. Nursing Care Plans for Leukemia. Retrieved from https://www.nursingcenter.com/


